Pain during urination, burning in the urethra, erection problems and frequent going to the toilet are symptoms of the inflammatory process in the prostate. What is prostatitis? The disease is multifactorial, the etiology is due to a combination of provoking factors that lead to inflammation. In medical practice, pathology is classified depending on the course, pathogenesis and other aspects. Consider what causes lead to the disease, what symptoms manifest and how it is treated.
What is prostatitis?
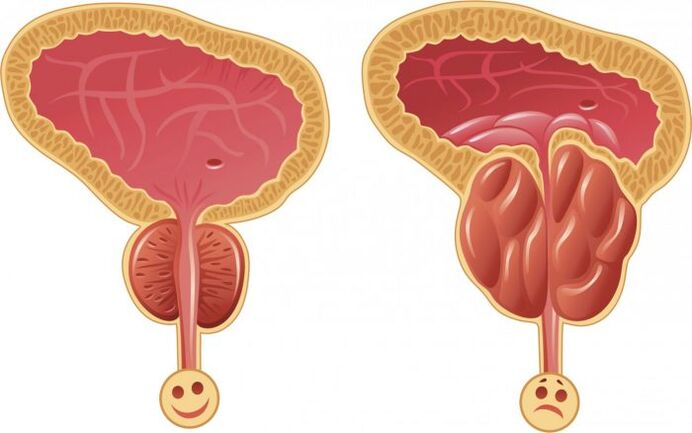
To understand what prostatitis is in men, you need to know which glandular organ it is. The prostate is a male internal organ. It looks like a "heart" or a "chestnut". Ancient doctors called this organ "another man's heart".
The functionality of the glandular organ is as follows:
- Production of secretion, which is a liquid with a specific odor;
- Protecting the prostate from infection;
- Maintaining full erectile function;
- Testosterone hormone synthesis;
- Ensuring a normal urination process.
The formation of secretions in the prostate is constantly observed. In healthy representatives of the stronger sex in the urethra enters the process of secretion of sperm. Prostate secretion increases the volume of semen, contributes to maintaining the vital activity of sperm.
For your information, prostatitis is a common disease that is diagnosed in 80% of men, of which 30% are diagnosed at the age of 20-40. According to static studies, pathology is observed in every tenth man.
If the ultrasound examination reveals swelling of the prostate, foci of inflammation in it, then it is prostatitis. In most clinical pictures, the inflammatory process goes hand in hand with the formation of stones. The male organ is surrounded by the urethral canal and seminal ducts, and edema leads to compression of the ureter. As a result, the dominant symptom of the disease is revealed - problems during urination - pain, cramps, tingling.
When an inflammatory process occurs, the qualitative and quantitative composition of prostate juice changes, resulting in a decrease in sexual desire, worsening of erections and a decrease in potency.
Causes and symptoms of prostatitis

Speaking of prostatitis, it is impossible to name the exact cause of the inflammatory process. Many physicians agree that the etiology is based on a combination of certain factors.
The occurrence of prostatitis is due to the following reasons:
- Infectious pathologies transmitted during intercourse.
- Violation of blood circulation in the pelvic organs. This leads to an inactive lifestyle, overly tight underwear, jeans.
- Injury to the organs of the perineum, causing poor circulation.
- Frequent hypothermia, the presence of chronic pathologies of the reproductive system.
- Hormonal imbalance, irregular sex life, prolonged abstinence.
- Inflammation in the rectum can cause the development of prostatitis.
- Constipation of a chronic nature.
- Decreased immune status. Primary sources include chronic stress, unhealthy eating habits, alcohol consumption, smoking, unbalanced diet.
- Urological infections such as gonorrhea.
In fact, there are many reasons to start the pathological process. Only by establishing the provoking factor can we talk about a favorable prognosis.
Prostatitis is both acute and chronic. In the first case, the man's body temperature increases significantly, frequent visits to the toilet are observed, followed by severe pain syndrome and weak pressure of urine flow. Often such a clinic is accompanied by burning in the perineum, painful sensations in the rectum during bowel movements.
Worth to know:with purulent inflammation of the prostate and the opening of an abscess, purulent masses are released from the urethral canal or rectum.
In the chronic course of the pathology, the symptoms are not very pronounced. Patients are diagnosed with the following clinic:
- Low temperature, which does not decrease for a long time;
- Pain in the pubic area;
- Bowel emptying problems;
- Constant fatigue, unreasonable nervousness and irritability.
Difficulty urinating is a special danger in the background of inflammation in the glandular organ. In the absence of adequate treatment, this can lead to serious consequences - acute urinary retention.
Types of prostatitis
So, to learn all about prostatitis in men, you need to consider the forms of the disease. First of all, there is an acute and chronic inflammatory process. The name "sharp" speaks for itself. This indicates that there is an inflammatory process caused by infections. In most cases microbes, somewhat less often the simplest microorganisms or fungi.
In the absence of therapy for the acute form of the pathology, it turns into a chronic course, can give a complication in the form of benign hyperplasia of the glandular organ. The symptoms do not manifest suddenly, which is a danger of this type of disease.
The etiology of chronic prostatitis is a consequence of pathogenic microorganisms and other causes. For example, the phenomenon of stagnation in the pelvic organs, age-related changes.
Important:bacterial prostatitis is acute and chronic. Inflammation is caused by bacteria - Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterococci, Klebsiella. This type is most often diagnosed in men aged 20 to 40, compared to other types of prostatitis, it occurs in 5-10% of clinical pictures.
Other types of inflammation in the prostate:
- The calculous form of prostatitis is characterized by an inflammatory process that develops as a result of the formation of stones in the prostate. It is most commonly diagnosed in elderly patients who have neglected acute drug treatment. Neglected calculous disease leads to impaired reproductive function, infertility, impotence, adenomas and other complications.
- The stagnant form of the disease usually passes in a chronic form, the etiology is not contagious. The main reason is the stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs, for example, in the case of disturbed blood circulation in the pelvis or stagnation of prostate secretion due to irregular intimate life.
- Infectious disease develops due to the activity of pathogenic bacteria, in most images tests reveal E. coli. There is an acute and chronic course, the clinic is similar to bacterial species.
- The purulent form is the most dangerous type of pathology. In medicine, purulent prostatitis is classified into other types. Catarrhal develops against the background of a weak immune status, along with the progression of sore throat and flu. Follicular prostatitis is already the second stage of purulent disease; there is a discharge of pus into the prostate, which is accompanied by a syndrome of severe pain and high body temperature. The parenchymal form is a severe form that requires timely treatment. With an abscess of glandular tissue, they speak of an abscess disease; therapy should be started immediately as there is a risk of sepsis.
The treatment regimen for prostatitis is a consequence of a certain type of pathology, ie it can differ significantly. You can combine medications with physiotherapy procedures and alternative therapies.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
To diagnose inflammation, the doctor collects the patient’s medical history and then prescribes laboratory and instrumental research methods. They allow, based on certain indicators, to make a diagnosis without errors.
Fact:you may suspect prostatitis by rectal examination of the prostate. Pain in the front of the rectum and an increase in the size of the organs are characteristic signs of inflammation.
After palpation of the rectum, the following diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound examination reveals the size of the organs, symptoms of the inflammatory process, changes in the structure of soft tissues;
- The study of prostate secretion allows you to recognize its composition and deviations from the norm;
- Examination of urine and smears from the urethral mucosa will help identify infectious diseases that are transmitted during sexual intercourse;
- Assessment of hormonal status. An excessive amount of hormonal substances can lead to pathological proliferation of glandular tissue, and a decrease in the concentration of the hormone can lead to its malfunction.
In the diagnosis of a medical specialist, the inflammation itself is not interested, since it can be detected by palpation of the prostate, but the causes of the disease. Finally, determining the correct provoking factor allows you to prescribe an effective course of therapy.
Methods of treating the disease
Treating prostatitis is always a complex process that involves taking various medications. It is not forbidden to use traditional methods of therapy with a doctor's permission.
Therapeutic activities include the following:
- Antibacterial tablets, immunostimulating drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs. Dosage, frequency and duration of use are determined individually. Medications can be purchased at a pharmacy, many of which are needed with a prescription.
- Physiotherapeutic manipulations - use of magnetic field, leech therapy, ultrasound and laser treatment.
- Prostate massage. It enables you to strengthen the reproductive system, normalize blood circulation in the prostate and pelvic organs.
Traditional methods of therapy include decoctions and infusions based on medicinal herbs. Patient reviews note the high therapeutic efficacy of red root rhizomes, licorice and marshmallows.
Important:to cure prostatitis, you must strictly adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen. Self-administration of medications, even the most effective ones, may not give the desired result. There is no single therapy tactic: what helps one patient harms another.
Preventive actions
Prostatitis is one of those pathologies that is easier to prevent. Doctors have long developed preventive measures to rule out the disease. Prevention is primary and secondary. In the second case, it should prevent the recurrence of chronic disease.
Preventive actions:
- Physical activity;
- Regular sexual intercourse;
- Exclusion of promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- Timely treatment of all concomitant pathologies;
- Preventive examinations by a urologist;
- Rational diet, rejection of bad eating habits.
Prevention of prostatitis does not require much time and investment, and the effectiveness of the measures is undeniable.
Prostatitis is a common disease. The rate of self-healing is very low. Lack of appropriate therapy leads to a chronic course of the disease, which periodically worsens and can cause organ hyperplasia or oncology.































